By Matthew Brown and John Flesher
The Biden administration proposed bringing back rules to protect imperiled plants and animals on Wednesday as officials moved to reverse changes under former President Donald Trump that weakened the Endangered Species Act.
The U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service said it would reinstate a decades-old regulation that mandates blanket protections for species newly classified as threatened.
The blanket protections regulation was dropped in 2019 as part of a suite of changes to the application of the species law that were encouraged by industry, even as extinctions accelerate globally due to habitat loss and other pressures.
Officials also would no longer consider economic impacts when deciding if animals and plants need protection. And the rules make it easier to designate areas as critical for a species' survival, even if it is no longer found in those locations.
That could help with the recovery of imperiled fish and freshwater mussels in the Southeast, where the aquatic animals in many cases are absent from portions of their historical range, said Fish and Wildlife Service Assistant Director Gary Frazer.
Frazer said Wednesday's proposal would restore “baseline” protections so species don’t get pushed further toward extinction.
“We have the opportunity to try to improve the status of species before they get to the brink,” he said.
Details on the proposed rules, which could take a year to finalize, were obtained by The Associated Press in advance of their public release.
They'll face strong pushback from Republican lawmakers, who say President Joe Biden's Democratic administration has hampered oil, gas and coal development, and favors conservation over development.
“These proposed rules take us in the wrong direction and are entirely unnecessary given the proven track record of success from private conservationists and state and local land managers," said House Natural Resources Committee Chairman Bruce Westerman, a Republican from Arkansas.
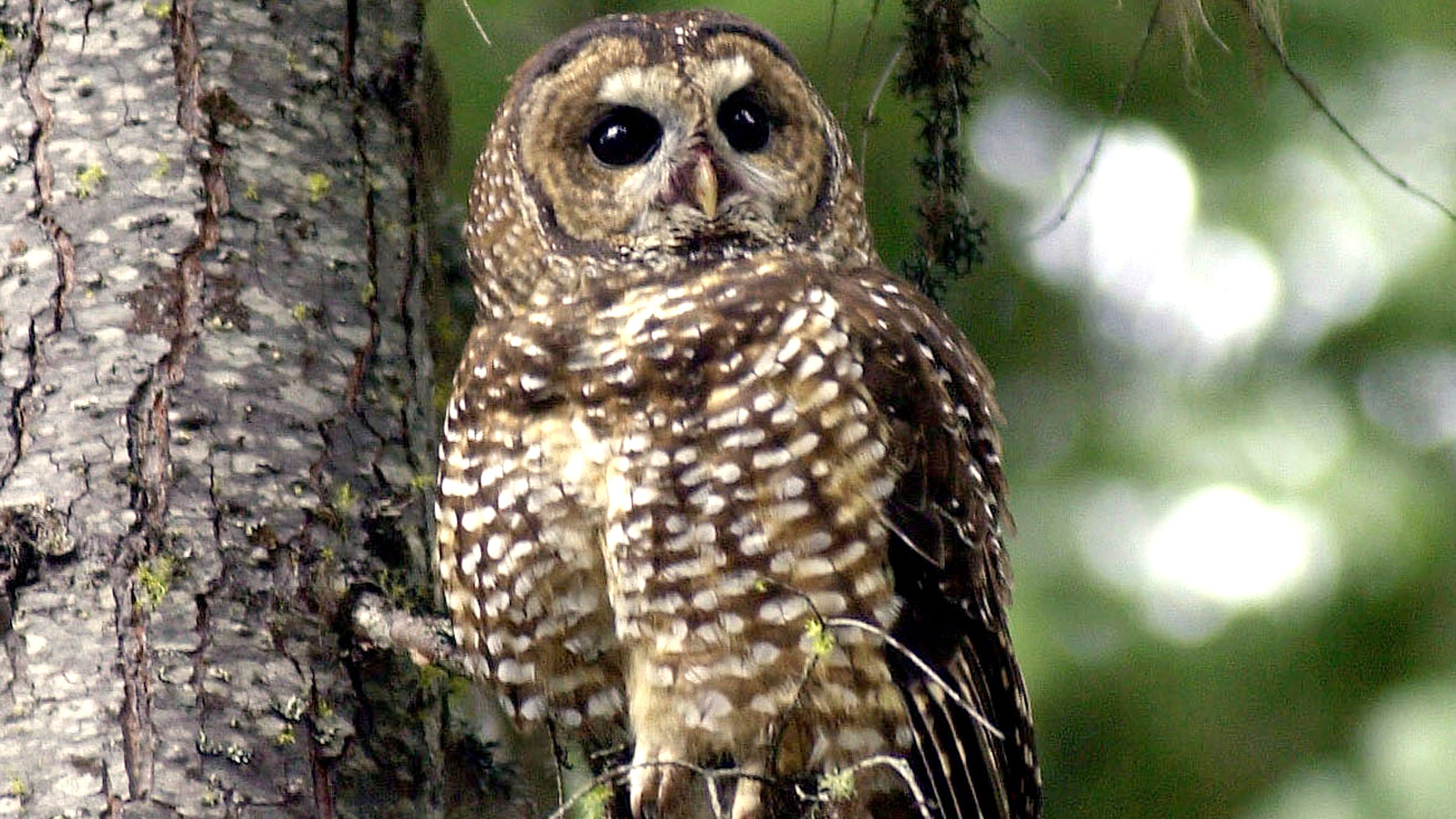
Industry groups have long viewed the 1973 Endangered Species Act as an impediment. Under Trump they successfully lobbied to weaken the law’s regulations as part of a broad dismantling of environmental safeguards. Trump officials rolled back endangered species rules and protections for the northern spotted owl, gray wolves and other species.
The spotted owl decision was reversed in 2021 after officials said Trump's political appointees used faulty science to justify opening millions of acres of West Coast forest to potential logging. Protections for wolves across most of the U.S. were restored by a federal court last year and the Biden administration has said it will decide by next February if they should remain in place.
Many of the changes under Trump were finalized during his last weeks in office.
Since then, officials imposed less restrictive protections for more than a dozen animals and plants compared to what they would have received, said Jonathan Wood with the Property and Environment Research Center, a free-market policy group based in Bozeman, Montana.
Wood said the Biden proposal could hurt state and private landowner efforts to recover species, by imposing more punitive regulations that undermine voluntary conservation incentives.
U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service Director Martha Williams said in a statement that the changes "reaffirm our commitment to conserving America’s wildlife and ensuring the Endangered Species Act works for both species and people.”
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Fisheries Assistant Administrator Janet Coit said the rules would ensure the species law remains effective as climate change alters habitats around the globe, and plants and animals become extinct.
The Biden administration had earlier withdrawn a 2020 rule that limited which lands and waters could be designated as places where imperiled animals and plants could receive federal protection. It also reversed Trump’s decision to weaken enforcement of the century-old Migratory Bird Treaty Act, which made it harder to prosecute bird deaths caused by the energy industry.
But environmentalists have been frustrated that it's taken more than two years for Biden to act on some of the Trump-era rollbacks. Stoking their urgency is the prospect of a new Republican administration following the 2024 election that could yet again ease protections.
“These are promising steps to get us back to the Endangered Species Act's purpose, its power to protect,” attorney Kristen Boyles with Earthjustice said of the new rules. The group sued on behalf of environmental groups to block the Trump rules and prevailed in U.S. District Court then lost on appeal.
Other environmentalists complained that some Trump-era changes would remain intact.
One requires agencies to protect living spaces for imperiled species only when development would harm an entire habitat and not just part of it. That could remove obligations to fix damage from logging trees that are needed by spotted owls unless all of their 9-million-acre habitat zone were affected, said Stephanie Kurose at the Center for Biological Diversity.
Biden’s proposal also retains a Trump change allowing agencies to approve projects without guarantees habitat harms will be reduced.
“This makes it easier to authorize piecemeal destruction of critical habitat,” said McCrystie Adams with Defenders of Wildlife.
An array of industry groups have long maintained that economic impacts are not given enough consideration in U.S. government wildlife decisions. Those groups range from livestock and ranching organizations to trade associations representing oil, gas and mining interests.
The Endangered Species Act is credited with helping save the bald eagle, California condor and scores more animals and plants from extinction since President Richard Nixon signed it into law. It currently protects more than 1,600 species in the United States and its territories.
Flesher reported from Traverse City, Michigan.